Testing Car Battery Health: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’ve ever wondered how to test a car battery’s overall health, you’re in the right place. Your car’s battery is what provides the electrical power needed to start the engine and operate various components. So, ensuring its health is crucial for a smooth and uninterrupted driving experience. In this article, we will walk you through some simple yet effective methods to gauge the health of your car battery. With a few easy steps, you’ll be able to assess if your battery is in good condition or if it might be time for a replacement. So, let’s dive in and understand how to test a car battery’s overall health.
How to Testing Car Battery Health?
Testing the overall health of your car battery is essential for ensuring its optimal performance and reliability. Regular battery checks can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems, saving you time, money, and frustration. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various methods that can help you test your car battery’s overall health effectively.
1. Visual Inspection
The first step in testing your car battery’s health is to conduct a visual inspection. Look for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or leaks. Here’s what you need to check during a visual inspection:
- Inspect the battery case for cracks or bulges.
- Check the battery terminals for corrosion, rust, or buildup of dirt.
- Ensure that the battery cables are properly connected and secure.
- Look for any signs of acid leakage around the battery.
If you notice any of these issues, it may indicate a battery problem that requires further testing or professional assistance.
2. Battery Voltage Test
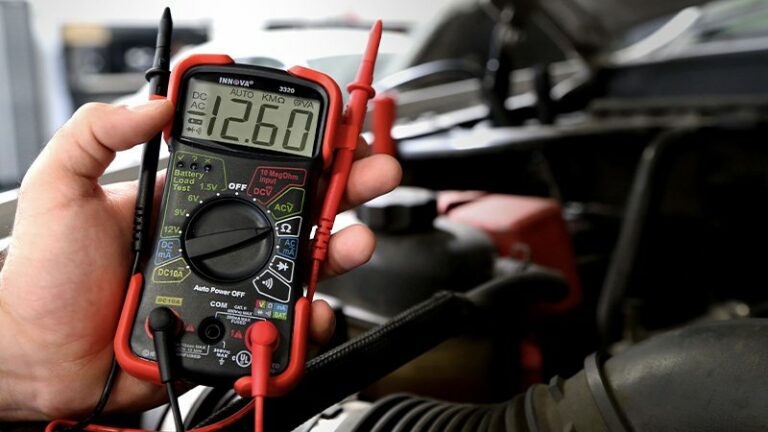
One of the simplest ways to assess a battery’s health is by measuring its voltage. Here’s how you can perform a battery voltage test:
- Make sure the engine is turned off and all electrical devices are switched off.
- Locate the battery and identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals.
- Use a digital multimeter and set it to the DC voltage range.
- Connect the positive (red) multimeter probe to the positive battery terminal and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal.
- Observe the voltage reading on the multimeter display.
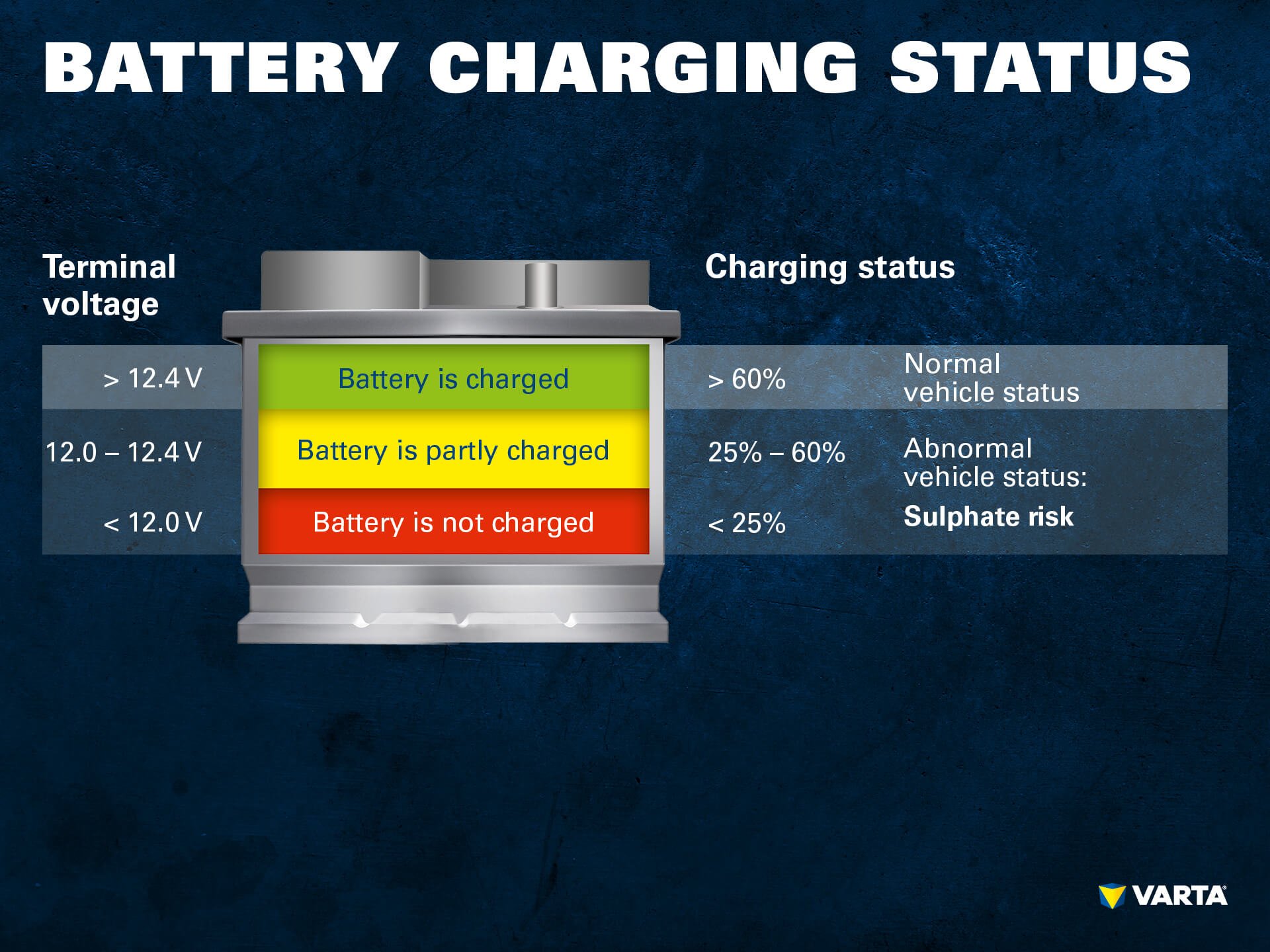
- A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. Anything below 12.2 volts indicates a weak or discharged battery.
3. Load Test
A load test helps determine a battery’s ability to hold a charge under a simulated load. This test gives a more accurate assessment of the battery’s performance and overall health. Follow these steps to conduct a load test:
- Ensure the battery is fully charged before performing the test.
- Disconnect any devices connected to the battery.
- Connect a load tester to the battery according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Apply the load by pressing the tester’s load button or switch.
- Monitor the voltage for a specific duration (usually around 15 seconds).
- An acceptable voltage drop during the test is typically around 9.6 volts or above. Anything lower indicates a battery that may need replacement.
4. Conductance Test
A conductance test assesses the internal condition of the battery and provides a measure of its ability to deliver power. Many modern battery testers use conductance technology to evaluate battery health quickly. Here’s how to perform a conductance test:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to connect the conductance tester to the battery.
- Initiate the test and wait for the results.
- The tester will provide a conductance value, usually displayed as CCA (Cold Cranking Amps).
- If the CCA value is significantly lower than the battery’s rated CCA, it indicates a weakened battery that might require replacement.
5. Hydrometer Test (for Filler Cap Batteries)
If you have a traditional battery with filler caps, you can perform a hydrometer test to assess the specific gravity of the electrolyte. This test helps determine the state of charge and overall health of the battery cells. Follow these steps to conduct a hydrometer test:
- Put on safety goggles and gloves before handling the battery.
- Carefully remove the filler caps from the battery.
- Insert the hydrometer’s nozzle into each cell and draw enough electrolyte to fill the hydrometer’s chamber.
- Read the specific gravity value on the hydrometer.
- A fully charged battery typically has a specific gravity reading between 1.265 and 1.299. Any values below indicate a weak or discharged battery.
6. Diagnostic Scan Tool Test
If your vehicle has an onboard diagnostic system (OBD-II), you can use a diagnostic scan tool to check the battery’s health. Follow these steps:
- Locate the OBD-II port in your vehicle (usually under the dashboard).
- Plug the diagnostic scan tool into the OBD-II port.
- Turn the ignition key to the accessory position without starting the engine.
- Select the battery health option on the scan tool’s menu.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the battery test.
- The scan tool will provide a detailed report on the battery’s health, including voltage, capacity, and CCA.
7. Electrolyte Indicator Test
For batteries equipped with a built-in electrolyte indicator, you can use it to assess the overall health of the battery. Follow these steps:
- Locate the built-in indicator typically located on top of the battery.
- Observe the indicator’s color (usually green, black, or clear).
- A green indicator often indicates a healthy battery with sufficient electrolyte.
- A black or clear indicator may suggest a battery with low electrolyte level, which requires further attention.
8. Professional Battery Testing
If you’re unsure about conducting battery tests yourself or suspect a more significant issue, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance. Certified technicians have access to advanced testing equipment and can provide a detailed analysis of your battery’s health and state of charge.
9. Regular Maintenance Tips
Apart from conducting battery tests, regular maintenance is crucial for prolonging the life and ensuring the health of your car battery. Consider the following tips:
- Clean the battery terminals regularly to prevent corrosion.
- Tighten any loose connections to ensure proper electrical contact.
- Inspect the battery case for cracks, bulges, or other signs of damage.
- Keep the battery and surrounding area clean and free from dirt and debris.
- Ensure that your vehicle’s charging system is in optimal condition.
- Avoid excessive idling, as it can strain the battery.
- If your vehicle will be unused for an extended period, consider using a battery tender or disconnecting the battery to prevent gradual discharge.
10. Safety Precautions
When testing your car battery’s health, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Follow these precautions:
- Always wear safety goggles and gloves when handling the battery.
- Avoid smoking or using open flames near the battery.
- Ensure the engine and all electrical devices are turned off during tests.
- Do not attempt to test a frozen or damaged battery.
- If electrolyte comes into contact with your skin or eyes, flush with clean water immediately and seek medical attention if necessary.
Regularly testing your car battery’s overall health and implementing proper maintenance measures will help ensure a reliable and functional vehicle. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can assess your battery’s condition accurately and take appropriate action if needed.
Testing Battery Health in Your Car, Truck or SUV
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I test a car battery’s overall health?
To test a car battery’s overall health, you can perform the following steps:
What tools do I need to test a car battery’s overall health?
To test a car battery’s overall health, you will need the following tools:
Can I test a car battery’s health without any tools?
While it is recommended to use specific tools, you can perform a basic test without them. Start the car’s engine and turn on the headlights. If the lights are bright and steady, the battery is likely in good health. However, if the lights are dim or flickering, it may indicate a weak battery.
How can I test a car battery’s voltage?
To test a car battery’s voltage, you need a multimeter. Set the multimeter to DC volts and connect the positive (red) probe to the battery’s positive terminal and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
How can I test a car battery’s cranking amps?
To test a car battery’s cranking amps, you can use a load tester. Connect the load tester to the battery following the manufacturer’s instructions. Apply a load to the battery and check the reading on the tester. A healthy battery should provide the specified cranking amps for your vehicle.
What do I do if my car battery fails the tests?
If your car battery fails the tests or shows signs of weakness, it may need to be replaced. Consult a professional mechanic or visit a local auto parts store for a new battery and assistance with installation.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, testing a car battery’s overall health is crucial for ensuring its reliability and preventing unexpected breakdowns. By following simple steps such as conducting a voltage test, load test, and inspecting for any physical damage, drivers can assess the battery’s condition and take necessary actions such as charging, replacing, or seeking professional assistance. Regular battery testing and maintenance not only enhance the battery’s performance but also contribute to the longevity of the entire vehicle system. Therefore, understanding how to test a car battery’s overall health is essential for every car owner’s peace of mind and smooth driving experience.